Back to Research & Demonstration
Comparison of pasture fertilization strategies
Project Details
Project Lead: Manitoba Beef & Forage Initiatives
Collaborators: Harvey Dann (Alert-Agri), John Heard (Manitoba Agriculture)
Years: 2019-2022
Project Status: Complete
Funding & In-Kind Support: Canadian Agricultural Partnership, Heritage Co-op
Location: First Street Pasture
Scope: Demonstration
Keywords: Fertility Management, Forage Rejuvenation
Approach
Investigate two fertilization strategies for differences in pasture forage yield and composition, differences in forage quality, differences in residual effects on the soil, and differences in cost of practice.
Key Findings
Forage yield and composition:
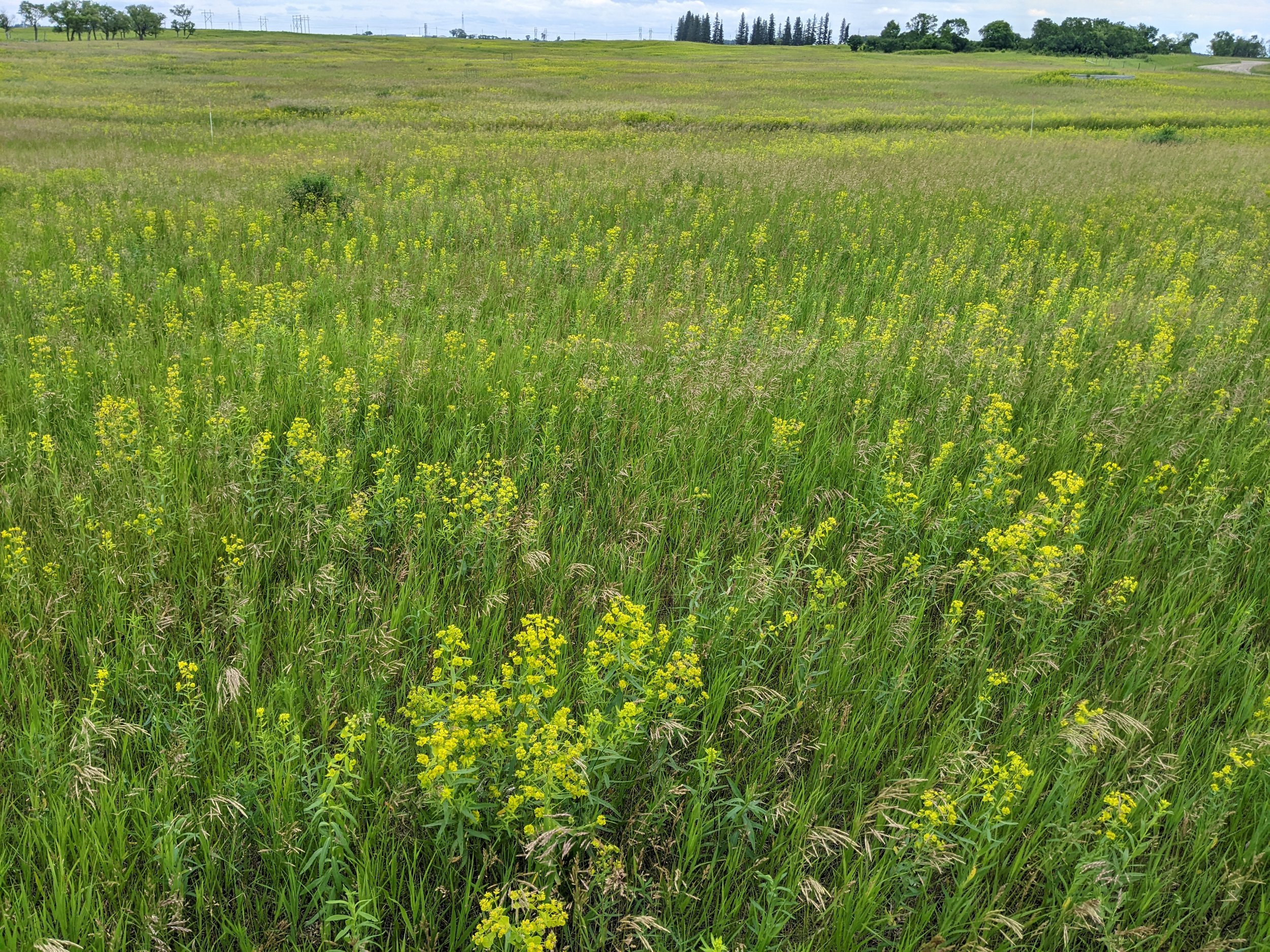
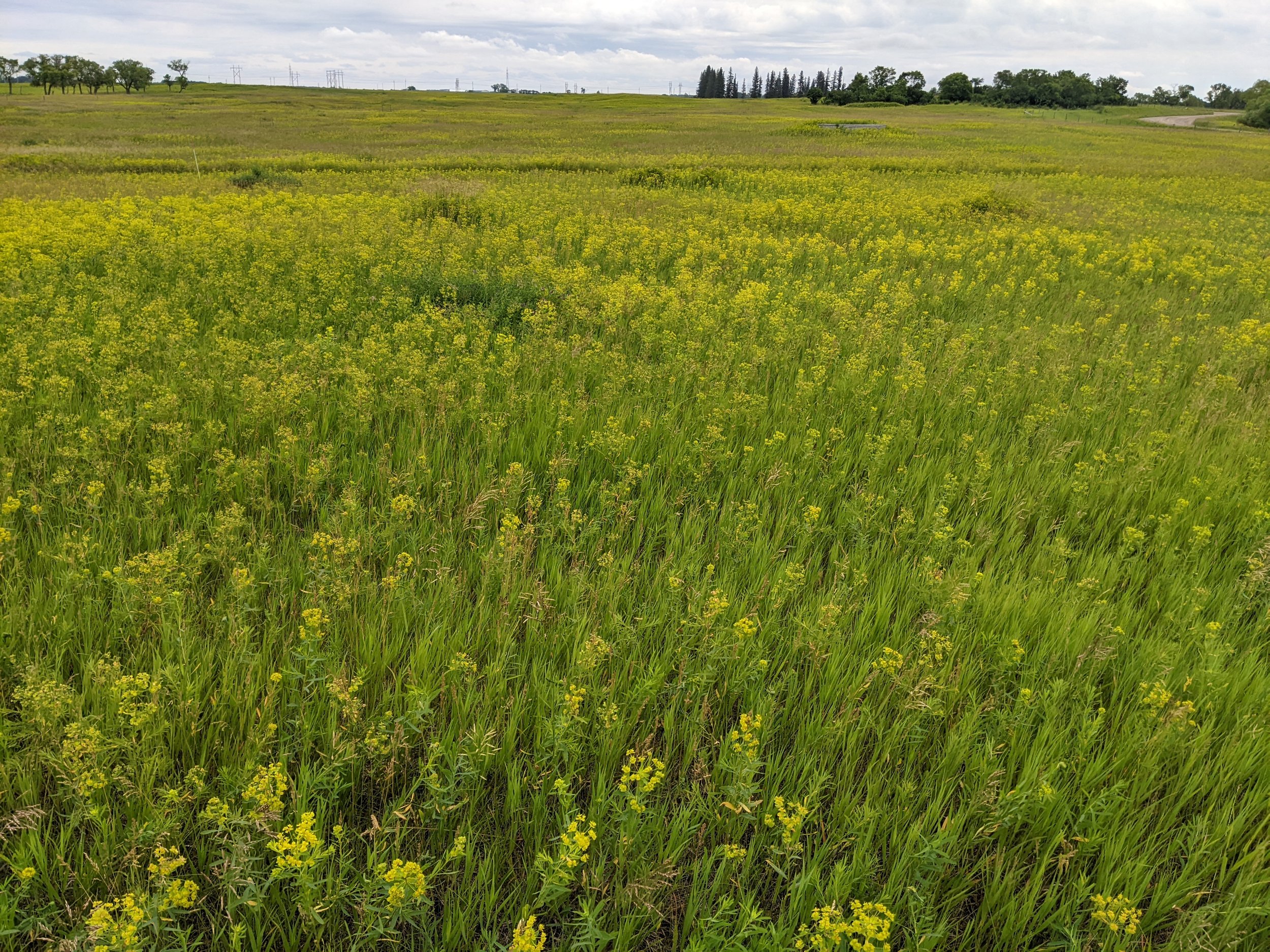
Applying conventional fertilizer increased abundance of leafy spurge
Pedogenesis fertilizer did not impact abundance of leafy spurge
Neither fertilizer impacted overall yield
Forage quality:
Fertilizer did not impact crude protein, total digestible nutrients, or fibre.
Fertilizer did not impact calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, potassium, or sodium.
Foliar cover and yield across fertilizer treatments.
Residual effects on soil:
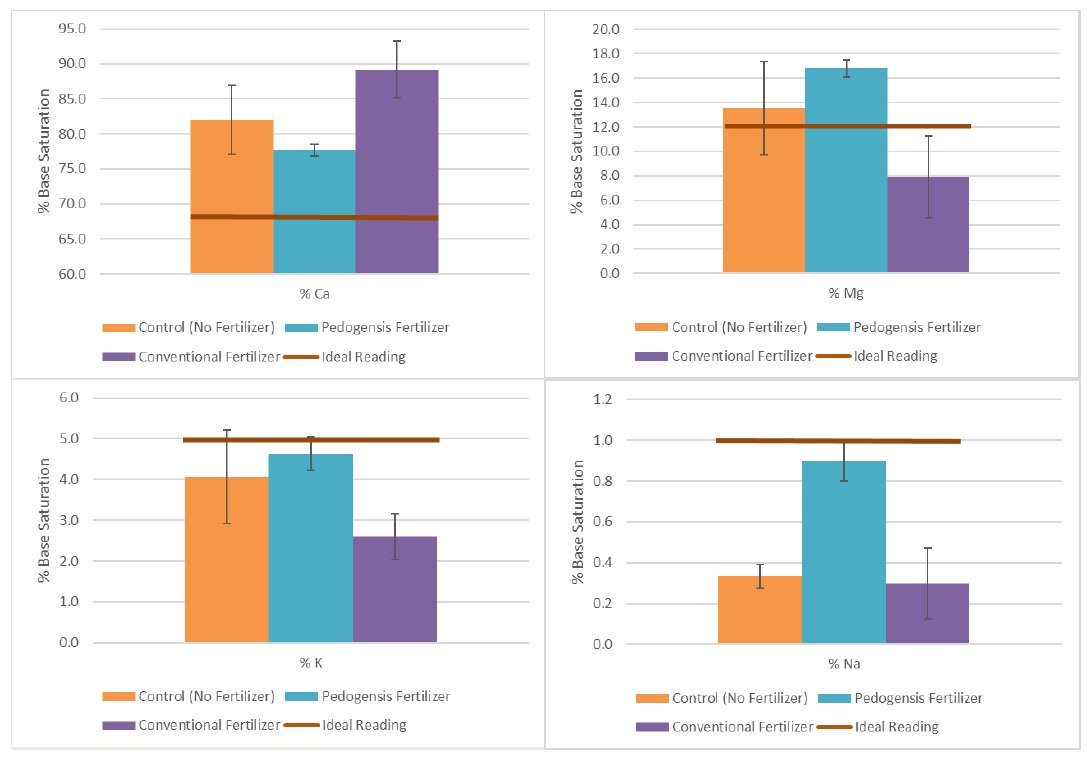
The Pedogenesis fertilizer impacted base saturation cation ratios but did not raise or lower any one cation to the ideal reading.
There is very little difference in soil organic matter, nitrate, phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, potassium, boron, copper, or zinc between treatments.
The Pedogenesis treatment showed increases in sulfur, manganese, sodium, and iron compared to the control and conventional fertilizer treatments.
Cost of practice: The Pedogenesis product has a higher per acre cost than a conventional fertilizer.
Long term effects: No long term effects were found in 2022 for forage yield, forage quality, or residual effect on soil.
Base cation saturation ratio of calcium (top left), magnesium (top right), potassium (bottom left), and sodium (bottom right). Idea Readings are provided by Pedogenesis.
Full Reports:
Related Projects at MBFI:
Industry Resources:
Soil Fertility Guide - Manitoba Agriculture
Soil Cation Ratio Vs Sufficiency Levels - Michigan State University Extension